Perfect hydration: the secret to energy and vitality not just for athletes
Proper hydration is essential for performance and recovery – not only in sport. In this article, you’ll find out when and why the body needs more than just water or tea. We’ll share which supplements to choose and what to look out for when buying. We’ll finish by comparing a few options.
Article contents
Understand proper hydration for the body
In everyday life, the body loses fluids with only a minimal loss of electrolytes, which it can easily replace through food. However, there are situations where it can’t cope with a greater loss. In these cases, it’s important to replace not only water, but also electrolytes.
When an imbalance can occur
- excessive sweating,
- high body or ambient temperature,
- intense exercise,
- physical changes,
- severe vomiting or diarrhoea,
- taking certain medicines,
- illness leading to
- disruption of the mechanisms that regulate water balance,
- increased fluid excretion,
- for example, people with diabetes may pass more urine,
- drinking too much water,
- prolonged fasting.9
How to stay hydrated and replace electrolytes – practical tips for every day
The need to replace fluids and electrolytes is highly individual. During intensive training in a hot environment, the body can lose up to two litres of sweat. Under normal conditions, it’s typically around half a litre.
The main components of sweat are:
- water,
- electrolytes:
- sodium and chloride in tens of mmol/l,
- potassium in units of mmol/l,
- calcium and magnesium in trace amounts,
- waste products,
- other substances (lipids, glucose, spices,...)9
With foods, we use the glycaemic index to see how quickly blood sugar rises. For drinks, there’s a hydration index, which shows how quickly they are excreted compared to water. Drinks that contain sodium have a higher hydration index. The same applies to drinks containing macronutrients.2,6
How to replace electrolytes, improve performance and speed up recovery
- A varied diet - a diet rich in fruit, vegetables, dairy products, nuts, seeds, grains and legumes is a natural source of electrolytes. For example, a snack of a roll with creamy fresh cheese, pumpkin seeds and a banana is a great source of sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium.
- Coconut water - a natural source of potassium, calcium, magnesium and sodium. Thanks to its mineral content, it’s a good option for topping them up.3
- Mineral-rich salts - standard table salt is refined and is mainly a source of sodium and chloride (NaCl), sometimes with added iodine. In the kitchen, consider using other salts that contain minerals, such as sea salt or unrefined rock salt. Even trace amounts of minerals have a positive effect on the body and contribute to normal function. As these are unrefined forms, choose trusted makers that focus on quality and test for microplastics and heavy metals. Redmond Real Salt from an underground mine in Utah is an easy addition to everyday cooking.
- Electrolyte drinks - there’s a wide choice on the market. Do you need to replace minerals after a demanding training session, or simply rebalance lighter electrolyte losses? The right choice can help with hydration, performance and recovery. At the end of this article, you’ll find a comparison of our favourites.12
- Beetroot - in team sports where high-intensity activity is interrupted, drinking beetroot juice can lead to improved performance. This is linked to the nitrite and nitrate content, which can lower blood pressure. Studies have also shown positive effects on performance and recovery in alpine skiers.4,5
Electrolyte drinks: what to watch for, and when they can do harm
Electrolytes and drinks that contain them are becoming increasingly popular. Another term you may see for electrolytes is a sports drink. You can choose from dissolvable powders, tablets you drink with water, or ready-to-drink options. Every electrolyte drink is different.
When should you have an electrolyte drink?
The need depends on the source of the electrolyte and fluid imbalance (see above). Intensive athletes training for around an hour or more may benefit from these supplements. Evidence shows that adequate hydration before and during sport supports sufficient blood volume and extends sustained performance. 1
Can electrolyte drinks be harmful?
Whether they can be harmful for you depends on your health and their composition. Key ingredients are typically sodium, potassium and sometimes an energy source in the form of simple sugars.
Sodium can be a complication for people with high blood pressure, or other conditions that require sodium restriction. Sodium draws water into the bloodstream. This also increases blood volume and blood pressure. The amount of sodium is often too high compared with the amount lost and the recommended intake.
Taking electrolytes without a prior loss can lead to over-supplementation and cause toxicity (poisoning) in the body. High levels of potassium (hyperkalaemia) can lead to diarrhoea or vomiting and cause dehydration.
Another common component in these drinks is an energy source in the form of simple sugars. For an intensive athlete, this may help with faster recovery. In general, it increases energy intake from sugar, which isn’t always desirable. It can also be a complication for people with insulin sensitivity issues or those living with diabetes.9
Electrolyte supplements under the microscope: 6 tips on what to look out for in the ingredients
- Sweetener
- Most electrolyte drinks contain simple carbohydrates. These are a quick energy source, so it’s worth considering whether you want them. These carbohydrates can come from different sources - glucose, sucrose, corn syrup, fructose. At the same time, glucose in electrolyte drinks helps water absorption in the body.
- Artificial sweeteners
- add flavour without excess energy.
- Commonly used aspartame is carcinogenic in rodents. According to the WHO, it falls into Group 2B - "Probably carcinogenic to humans". Even so it is still permitted as a food additive.7, 18
- Colourings
- They are not an essential part of a drink, but they make it more visually appealing.
- According to studies, artificial colourings are linked to the development of tumours in various organs.8
- Mineral content and ratio
- Choose based on the body’s individual needs and the intended use.
- Fillers
- Based on the principle that “bulk makes an impression“. These are substances with no added value that simply increase the product’s volume.
- Source
- In other words, the form an electrolyte is in. This affects the uptake of the element. In general, it’s recommended to look for chelated (organic) or liposomal forms. In a chelated form, the substance is bound to amino acids, which protect the element from unwanted interactions in the body (for example, with phytates). In the name you’ll see terms such as bisglycinate, citrate, malate, gluconate. A liposomal form offers better uptake of the substance, transported through the body in a lipid “capsule” called a liposome. 10,11
- Supportive ingredients
- These are substances that affect uptake either negatively (inhibitors, antagonists) or positively.
- Inhibitors reduce uptake. Examples include phytic acid (beans), oxalic acid (spinach), tannins (coffee, tea), or fibre.
- Antagonists are substances that are absorbed via the same transporter. At higher doses of one, absorption of the other can decrease. For example, calcium with phosphorus/zinc/iron.
- Supportive substances, on the other hand, help uptake. For example, vitamin B6 or vitamin C and magnesium.9
- Content of other substances beneficial for the body (vitamins, minerals).
Comparison of electrolyte supplements
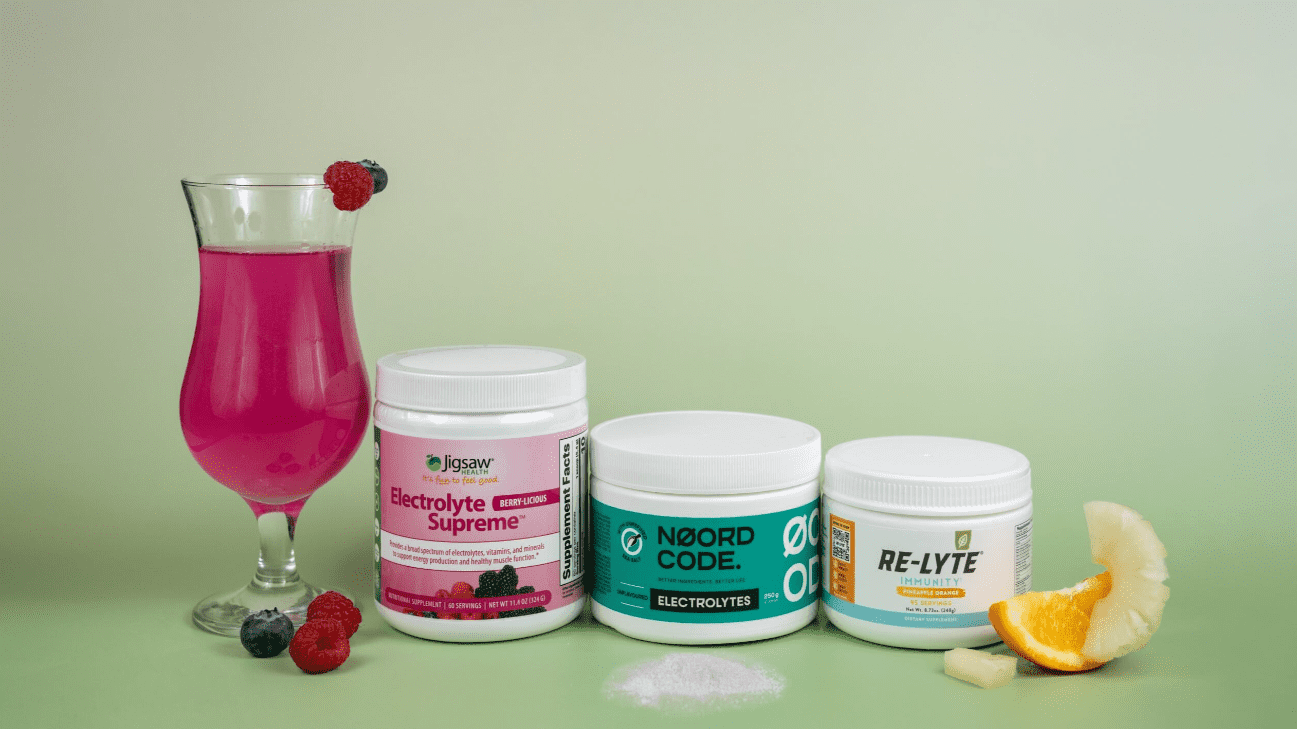
There’s a wide range of brands on the market focused on replacing electrolytes. We’ve picked out three standout products: Redmond, NoordCode and Jigsaw Health.
- Mineral blend: sodium, potassium (citrate), chloride, calcium (carbonate) and magnesium (malate and glycinate).
- Ingredient quality: Minerals in bioavailable forms for effective uptake. Contains Real Salt – sea salt mined from an ancient deposit in Utah. For easier mixing, it contains pharmaceutical-grade calcium carbonate, which in combination with citric acid converts to calcium citrate, which is gentler on digestion. Non-GMO.
- Unique features: No sugars or artificial sweeteners. Suits paleo, vegan and keto diets, as well as fasting. Contains dried coconut water.16, 17
- Mineral blend: sodium, potassium (citrate), magnesium (hydroxide)
- Ingredient quality: Sodium comes from Celtic sea salt, and magnesium from seawater. Pure minerals without unnecessary additives.
- Unique features: A European alternative to LMNT. Suits keto, paleo, vegans and fasting. Sugar-free, tested for heavy metals and microplastics. Made in Europe to complement a varied diet.14,15
JIGSAW HEALTH Electrolyte Supreme
- Mineral blend: a broad spectrum of electrolytes – sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium – complemented by a complex of B vitamins in active, bioavailable forms.
- Ingredient quality: Uses premium ingredients for maximum uptake and effectiveness.
- Unique features: Non-GMO, soy-free, sugar-free and gluten-free. Suits a keto diet. The aim is to turn ordinary water into a drink rich in minerals and vitamins.13

Electrolytes are important for the body. For everyday needs, a varied, balanced diet supports their regular intake. There are situations where food won’t cover depleted stores. Electrolyte and sports drinks can be grouped among special-purpose fluids and can be helpful for hydration and replacing minerals lost in specific situations. The same applies to other food supplements with electrolytes. Always check the ingredients and consider your health.
Did this article bring you useful information? Share it with your friends using the button below. If you don’t want to miss more news, subscribe to our updates and follow us on social media.
Under EU regulations, the blog can’t link to web pages with a promoted product. You can, of course, find the products on our website Pravé Bio.
Sources used
- Fluid intake is a strong predictor of outdoor team sport pre-season training performance. Online. Taylor & Francis Group. 2023. Available here.
- A randomized trial to assess beverage hydration index in healthy older adults. Online. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2019. Available here.
- Does coconut water help re-hydrate as well as sports drinks? Online. Consumerlab.com. 2019. Available here.
- Application of beetroot's nitrates juice in team sports Application du jus de nitrates de betterave dans les sports d’équipe. Online. Science Direct. 2023. Available here.
- Consuming Beetroot Juice Improves Slalom Performance and Reduces Muscle Soreness in Alpine Skiers under Hypoxic Conditions. Online. Science Direct. 2024. Available here.
- A randomized trial to assess the potential of different beverages to affect hydration status: development of a beverage hydration index. Online. Science Direct. 2016. Available here.
- Aspartame and cancer - new evidence for causation. Online. National Library of Medicine. 2021. Available here.
- Food Color Additives in Hazardous Consequences of Human Health: An Overview. Online. National Library of Medicine. 2023. Available here.
- KASPER, Heinrich and BURGHARDT, Walter. Výživa v medicíně a dietetika. Prague: Grada, 2015. ISBN 978-80-247-4533-6.
- New approaches, bioavailability and the use of chelates as a promising method for food fortification. Online. Science Direct. 2022. Available here.
- Effect of advanced chelate technology-based trace minerals on growth performance, mineral digestibility, tibia properties, and antioxidant status in two broiler strains. Online. National Library of Medicine. 2024. Available here.
- Effects of oral salt supplementation on physical performance during a half-ironman: A randomized controlled trial. Online. National Library of Medicine. 2016. Available here.
- How is Electrolyte Supreme different from other Electrolyte Replacements? Online. Jigsaw Health. 2024. Available here.
- NoordCode's Electrolytes formula explained. Online. Nord Code. 2023. Available here.
- Electrolytes Unflavoured. Online. Noord Code. Available here.
- Re-Lyte® Hydration Jar / Strawberry Lemonade. Online. Redmond. Available here.
- Why did you switch to calcium carbonate in Re-Lyte products? Online. Redmond. Available here.
- Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs, Volumes 1–138. (n.d.). IARC Monographs on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans – INTERNATIONAL AGENCY FOR RESEARCH ON CANCER. Available here.
ŠárkaShe devoted her education and professional life to the world of gastronomy and nutrition. After studying hospitality and human nutrition, she completed her training as a nutritional therapist, which gave her a well-rounded view of the link between food and health.
She now uses this knowledge mainly in caring for her kids.
She isn’t afraid of challenges and opportunities, believes in new beginnings, and values a sustainable lifestyle. Outside of work, she enjoys gardening, hiking, and above all, her family, which remains her biggest anchor in life.

.png)
